Oct 12 2010
3 Comments
Hungary’s worst-ever environmental disaster
The residents described « a mini-tsunami ». A toxic one.
Last Monday, the red mud reservoir of an alumina plant ruptured in Hungary, near Ajka, 165km west of Budapest. As a result, 1.1 million cubic meters of red mud wiped out several villages through waves more than 2 meters high. It flooded 40 square kilometers of land, including affluents of the Danube, then reached one of Europe’s longest river on Thursday morning. So far, 7 people have been killed, 1 is still missing, and more than 150 have been injured, mostly by chemical burns. The death toll is still expected to rise.
As we write these lines, surrounding villages are being evacuated as the structure threatens to break in another point, which would result in another 500 000 cubic meters flooding the area.
 The disastrous chemical accident has been declared Hungary’s largest and most dangerous environmental catastrophe, exceeding by far the 130000 cubic meters of cyanide-tainted water that spilled in 2000 in Baia Mare, Romania. Ten years later, traces of cyanide are still found in the area. It is worth noting that this cyanide was in a liquid form, therefore very quickly carried aways by the river whereas the thick red mud will sit there for years, sipping into the ground and reaching ground waters.
The disastrous chemical accident has been declared Hungary’s largest and most dangerous environmental catastrophe, exceeding by far the 130000 cubic meters of cyanide-tainted water that spilled in 2000 in Baia Mare, Romania. Ten years later, traces of cyanide are still found in the area. It is worth noting that this cyanide was in a liquid form, therefore very quickly carried aways by the river whereas the thick red mud will sit there for years, sipping into the ground and reaching ground waters.
Read More
 By Samarendra Das & Felix Padel
By Samarendra Das & Felix Padel

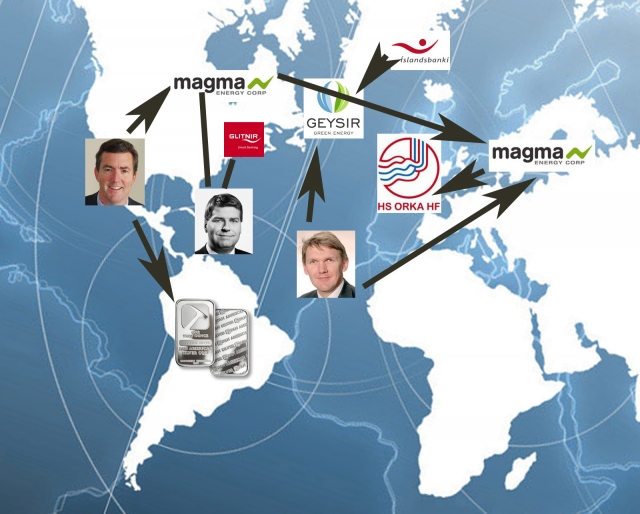 It has hardly escaped the attention of anyone living in Iceland of late, that the Canadian geothermal company, Magma Energy, recently bought Geysir Green Energy´s (another geothermal energy company) stock in HS Orka (southwest-peninsula power company), making Magma a majority stockholder with 98,5% partnership. Magma´s purchase of GGE´s stock comes as no surprise whereas it´s been clear from the onset that Magma intended to claim majority ownership over HS Orka.
It has hardly escaped the attention of anyone living in Iceland of late, that the Canadian geothermal company, Magma Energy, recently bought Geysir Green Energy´s (another geothermal energy company) stock in HS Orka (southwest-peninsula power company), making Magma a majority stockholder with 98,5% partnership. Magma´s purchase of GGE´s stock comes as no surprise whereas it´s been clear from the onset that Magma intended to claim majority ownership over HS Orka.
 Orissa is the most mineral rich state in India. It is green and fertile, a patchwork of tiny fields and thickly forested mountains with waterfalls tumbling over their red rocks. Like many of the world’s remaining areas of natural fertility, these mountains are largely populated by tribal peoples, which in India are called Adivasis – meaning literally ‘the original inhabitants’ – and are thought to be one of the oldest civilisations in the world. One quarter of the Orissan population are tribal, making it also the ‘poorest’ state in India according to the World Bank. But its figures judge well-being only by monetary exchange, and fail to mention that there has never been a famine recorded here, and that many Adivasis rarely use money, living in balance with the mountains, streams and forests which provide everything they need. In thanks for natures’ providence many Adivasi cultures worship the mountains on which they depend as Gods, and vow to protect their bountiful natural systems from damage. Some of the Orissan mountains are among the last ancient forest capped hills in India, thanks to the determination of tribal inhabitants against British colonial efforts to log them.
Orissa is the most mineral rich state in India. It is green and fertile, a patchwork of tiny fields and thickly forested mountains with waterfalls tumbling over their red rocks. Like many of the world’s remaining areas of natural fertility, these mountains are largely populated by tribal peoples, which in India are called Adivasis – meaning literally ‘the original inhabitants’ – and are thought to be one of the oldest civilisations in the world. One quarter of the Orissan population are tribal, making it also the ‘poorest’ state in India according to the World Bank. But its figures judge well-being only by monetary exchange, and fail to mention that there has never been a famine recorded here, and that many Adivasis rarely use money, living in balance with the mountains, streams and forests which provide everything they need. In thanks for natures’ providence many Adivasi cultures worship the mountains on which they depend as Gods, and vow to protect their bountiful natural systems from damage. Some of the Orissan mountains are among the last ancient forest capped hills in India, thanks to the determination of tribal inhabitants against British colonial efforts to log them.

 This article originally appeared in the June issue of the independent newsmagasine
This article originally appeared in the June issue of the independent newsmagasine