Aug 29 2012
6 Comments
Hellisheiði: A Geothermal Embarrassment
While driving Iceland’s national ring road, in a southerly direction from Reykjavík, one cannot miss noticing the steam coming up from an extraordinarily grey infrastructure covering a large piece of land around mount Hengill, approximately 30 km from the capital. Filled with roads, drills, pipelines, and a large powerhouse, this once untouched geothermal area is now the site of the Hellisheiði geothermal power plant, operated by the publicly owned Reykjavík Energy (“Orkuveita Reykjavíkur” in Icelandic, abbreviated “OR”), generating electricity almost entirely for aluminium production.
Geothermal energy is commonly praised as a “green” alternative to environmentally unfriendly power sources such as fossil fuels, coals and nuclear energy. As a result of “the development of what were once thought to be non-viable resources”, a glossy brochure from engineering firm Mannvit states, “more and more public and private entities are looking into geothermal power as part of their strategy to mitigate global warming while still meeting growing energy demands.” In a promotional text for the Geothermal Energy Exhibition at Hellisheiði, the plant is said to be a “striking example of how geothermal energy is harnessed in a sustainable manner in Iceland and a showcase for the rest of the world.” Additionally, Reykjavík Energy has not hesitated maintaining that “general public opinion of exploiting the geothermal resources in the Hengill region is positive.”
So many men, so many minds. Only about ten kilometres away from the plant stands the small town of Hveragerði, wherein one gets to hear a completely different story. “We cannot accept that OR will be permitted to continue polluting the atmosphere,” Hallgrímur Þ. Magnússon, clinical doctor in Hveragerði said to newspaper DV last June. A few days earlier he had voiced his worries to local newspaper Sunnlenska, encouraging the town’s residents to start taking magnesium and iodide supplements to counteract the health impacts of the power plant’s sulphur (hydrogen sulphide) pollution. “I maintain that the pollution is of such quantity that the human body needs those two materials in order to resist the effects,” Hallgrímur said to Sunnlenska.
Recent inspection makes it clear that the sulphur pollution, which does not only reach to Hveragerði but also to Reykjavík, often goes far above Icelandic and international standards. In the case of Hveragerði, the quantity of polluting materials in the atmosphere is such that the town should be considered within the plant’s dilution area (the area in which residential homes are not permitted).
EFFLUENT LAGOONS AND MANMADE EARTHQUAKES
Unfortunately for the burgeoning and PR heavy Icelandic energy sector, the green image of geothermal power has been repeatedly challenged lately. In particular regarding the country’s and, in fact, the world’s biggest geothermal plant at Hellisheiði. Two new unplanned effluent lagoons were recently discovered close to the plant, where waste water from geothermal pumping had leaked out onto the surface. Environmentalist and journalist Ómar Ragnarsson, who originally discovered the lagoons, followed the story by publishing his own photographs of similar lakes created by other geothermal plants, such as those by the plants at Reykjanes, Svartsengi, Nesjavellir and Bjarnarflag1. These lakes can be very dangerous to local freshwater systems, as Saving Iceland’s Jaap Krater and Miriam Rose explain in a book chapter on the development of geothermal harnessing in Iceland:
Geothermal fluids contain high concentrations of heavy metals and other toxic elements, including radon, arsenic, mercury, ammonia and boron, which are damaging to the freshwater systems into which they are released as waste water. Arsenic concentrations of 0.5 to 4.6 ppm are found in waste water released from geothermal power plants; the WHO recommends a maximum 0.01 ppm in drinking water.2
Yet another backlash for the geothermal industry is a recent study, carried out by Hanne Krage Carlsen, whose results were published in the international Environmental Research journal earlier this year3. The study shows a direct link between the plant’s sulphur pollution and increased purchase of asthma medicine among the residents of the greater Reykjavík area. New examination of vegetation in the Hellisheiði area also shows that the sulphur pollution has damaged large quantities of moss, which according to Magnea Magnúsdóttir who carried out the examination, will take decades to recover4. OR claims that the results of the plant’s Environmental Impact Assessment “indicate that construction of the plant will not have a lasting influence on the area’s vegetation” — something which, according to this recent information, needs to be questioned.
POLLUTION ABOVE GUIDELINE LIMITS
During OR’s Annual General Meeting (AGM) last June, it was revealed that Hveragerði is inside an area wherein sulphur (hydrogen sulphide) pollution is above the current guideline limits. New rules are supposed to go through in 2014, according to which the guideline limits will be strict 50 micrograms per square-meter per 24 hours. The authorities will also be obliged to alarm the public each time the pollution goes above that limit.
Though they admit the plant’s high concentration of polluting emissions, OR has said that the company will not able to adapt to the new rules until 2019 at the earliest. Therefore, the company will ask for an exception, to which the people of Hveragerði are heavily opposed. In an interview with Iceland’s National Broadcasting Service (RÚV), the town’s Mayor Aldís Hafsteinsdóttir protested against the company’s request, stating that OR had obviously rushed way too fast when preparing and building the plant and thus underestimated its environmental impacts. In a separate interview with Saving Iceland’s Miriam Rose this June, Aldís emphasized this point:
We feel very much like victims of all of this. This town has been here for 70 years and the power plant has only been here for 10 or 15. They should have considered the effects on the neighbourhood they were putting it in. It is absolutely obvious that the plant is situated too close to our town, as there are so many impacts that affect daily life here in Hveragerði.
Adding fuel to such criticism, Minister of the Environment Svandís Svavarsdóttir followed in the footsteps of many environmentalists and told RÚV, in an interview last June, that OR had been nothing but the puppet of heavy industry for the last years. That explains not only the company’s poor financial situation but also the environmental catastrophe at Hellisheiði, Svandís said. Mayor Aldís agrees: “They [OR] have sold their energy to the aluminium smelters way too cheap and now they can’t afford to reduce their pollution. That is, in my opinion, the reason why they are trying to stop the new regulations.”
DILUTION AREA: BIGGER THAN OF ALUMINIUM SMELTERS
The Hellisheiði plant started operating in 2006 and has since then seen two expansions, in 2008 and 2011, leading to increased sulphur pollution. Most of the energy goes to the aluminium smelter in Grundartangi, owned and operated by the North-American Century Aluminium, which then again is owned by mining and commodities giant Glencore.
Demonstrating Iceland’s haphazard approach to the development of geothermal energy, the Hellisheiði power plants’ dilution area has yet to be defined after six years of operation. However, it is clear from recent evidence that the dilution areas for geothermal plants should be much larger than for other polluting industries in Iceland — much bigger, for instance, than Rio Tinto Alcan’s aluminium smelter in Straumsvík and Century’s in Grundartangi, as reported by newspaper Morgunblaðið in June5. During OR’s recent AGM, their environmental director Hólmfríður Sigurðardóttir, admitted that she could not guarantee that the health of people living inside the area where pollution is above guideline limits (i.e. people living inside the dilution area) is not negatively affected by the pollution. Permanent residence is, in fact, prohibited inside such areas by law and land use is restricted to several limitations.
Interestingly, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) for the Hellisheiði power station, carried out by engineering firm VGK on behalf of OR, overlooked the potential impacts on Hveragerði altogether, though it did take into consideration the negligible impacts on Þorlákshöfn and other towns much further away from the plant.
In September 2011 more than 1500 earthquakes were felt in Hveragerði in a single day, with other quakes going on for several weeks, some up to 4 on the Richter scale6. At first OR denied any culpability in the incident, though the residents immediately recognised the quakes as being unusual as many were focused on a single spot. However, after a few days they admitted that they had been pumping geothermal effluent water back into the ground, which is necessary to prevent surface pollution, but is well known by geologists to be a cause of man-made earthquakes. OR responded to the resident’s outrage over the quakes by holding a public meeting in which they claimed they were simply speeding up the release of earthquakes that would have happened anyway in the future. To this local resident Einar Bergmundur stood up and stated: “That is a very good argument. I am also sure I am going to die one day, but that doesn’t give you the right to kill me today to speed the process up?”
THE GUINEA PIGS OF HVERAGERÐI
In January this year some residents of Hveragerði started experiencing breathlessness, coughing and nausea as well as a strong sulphurous smell. They called Aldís to ask what was going on. Thanks to a monitoring site the residents had requested OR to install on their kindergarten, Aldís was able to see that hydrogen sulphide levels had persistently been in the hundreds of micrograms for more than a week. One day they had reached 337µg, more than double the current regulations, and almost seven times higher than the new regulations would allow. With the man-made earthquakes still on their minds, the residents were furious. Aldís told us that despite this breach of regulations no action seems to have been taken by OR:
I just can’t believe that this is how it is supposed to be — that the locals are supposed to monitor these levels themselves. There must be some institution that is supposed to take care of the people and make sure that we are not breathing this. But it did not happen. We live here, we have kids, the elderly are fragile and some have bad lungs. They [OR] are experimenting with these technologies as they build the plants. If they wanted to use us, the inhabitants of Hveragerði as guinea pigs they should have asked us first and not let everything that has happened here come as a surprise. They must have known better before they started this project and that is a fact the makes us angry. Our experience of the Hellisheiði power plant teaches us that not a single plant should be built here in the vicinity before they have a complete control of those matters that have gone wrong in Hellisheiði.
In response to such criticism, OR published a press releases claiming that there are no health risks at that level of exposure and that much of the science which says so is contended. They invite people to visit the plant and breathe the fumes, and even suggest that up to 14,000µg of Hydrogen Sulphide is acceptable to breathe for up to 8 hours7.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) does not agree. They state that concentrations above 280µg can cause breathing problems, followed by eye irritation at 500µg, loss of energy and increased lactic acid in the blood at 700µg, and finally headaches, irritability, dizziness, memory loss and fatigue at 2800µg. By 14,000µg people tend to suffer “olfactory paralysis” — a shut down of sense of smell which prevents them from noticing the odour and accompanying dangers. The WHO recommends a maximum guideline of 150 µg/m3 for a 24 hour period to ensure “the absence of appreciable risks that can cause adverse health effects” whereas the Californian regulation limits Hydrogen Sulphide emissions to 43 µg/m3 for more than an hour to prevent strong smell8. Iceland’s current regulations are weak by international standards and even these weak standards are not being enforced.
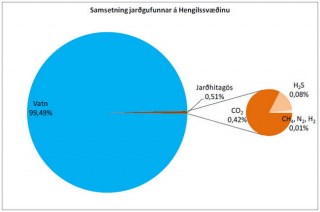
In the same press release OR presented a diagram of emissions from Hellisheiði showing that 99.49% of the steam released from the power plant is made up of water, while only 0.42% is CO2 and 0.08% Hydrogen Sulphide. This is a clear attempt at greenwashing the reality, as it is self evident that steam is largely made up of water and that this is not how sulphur concentrations in the environment are measured. These widely broadcast figures try to downplay well established science in what Aldís called “an insult to the intelligence of the people of Hveragerði.”
REYKJAVÍK’S CITY COUNCIL OPERATING AGAINST ITS OWN POLICY
Yet another 90 MW expansion is now planned in the area of Hverahlíð, south of the Hellisheiði plant and even closer to Hveragerði. The Hverahlíð plant is supposed to generate energy for another Century smelter, which currently stands half built and collecting dust in Helguvík, close to the Keflavík International Airport. The Helguvík project has been criticised from the beginning of its construction in 2008, not only for environmental reasons but also for the major energy uncertainty the project has long faced. During the smelter’s ceremonial first shovelling — interrupted by Saving Iceland activists who rightly named it “Century’s Lack Of Permission Party” as the company did not have any permissions but to construct the building itself — Century’s director in Iceland, Ragnar Guðmundsson, said that he hoped the energy issues would be sorted in late 2010, when the smelter’s first phase would be complete.
Today the unfinished building stands like a skeleton at the construction site while the energy issue remains unsolved. Century has signed contracts with two energy companies, OR and HS Orka — the latter owned mostly by Canadian firm Alterra Power and partly by Icelandic pension funds — but neither company has been able to guarantee any energy. HS Orka hopes to be allowed to drill in the geothermal areas of the Reykjanes peninsula — a large-scale construction that would not only permanently alter the peninsula’s unique nature, but also, as many scientists have claimed, not produce enough energy for the Helguvík smelter.
OR, on the other hand, bets on Hverahlíð as an electricity supplier for Helguvík. But the company is heavily indebted after its recent aluminium adventures, which is one of the reasons the contract with Century should be breached, says Sóley Tómasdóttir from the Left Green party (“Vinstri græn”) and board member of OR. In an interview with RÚV in April this year, she maintained that the company should focus on the environmental impacts at Hellisheiði before even thinking about building new plants. She also criticised the current majority of Reykjavík’s city council (composed of the social democratic “Samfylkingin” and the centrist “Besti flokkurinn,” a new party that won the city elections in 2010), for not standing by its promises to stop selling new power from the publicly owned energy company to heavy industry projects.
In the same interview, Haraldur Flosi Ólafsson, chairman of the board, responded to this criticism by maintaining that despite the current majority’s official opposition to developing any further energy for aluminium production, the company would have to abide to already existing contracts. The Century contract is originally from 2006 but was renewed in late December 2008, less than three months after Iceland’s infamous economic collapse. At the aforementioned AGM, Haraldur’s words were echoed by the company’s director Bjarni Bjarnason, who said that in his opinion all future plans for building new power plants should be abandoned, as building new plants for private entities goes against the company’s current policy. However, Bjarni stated, already existing contracts needs to be abided.
Sóley disagrees, pointing out a clause in the contract, which should allow for the company’s withdrawal if it does not have the financial capacity to fund the project. But instead of doing so, OR is now planning to finance the Hverahlíð plant with the assistance of Icelandic pension funds. Such a step is generally seen as very controversial (such as in the heavily criticised case of HS Orka) and as the first step on the way to the privatisation of Iceland’s nature.
NEITHER SUSTAINABLE NOR RENEWABLE
The impacts of sulphur pollution, man made earthquakes and effluent lagoons appearing at Hellisheiði are of great importance in Iceland in view of the large scale geothermal plans which are increasingly being promoted in Mývatn and Reykjanes peninsula. According to the recently published parliamentary resolution for the so-called Master Plan for Hydro and Geothermal Energy Resources in Iceland, these geothermal power plans are definitely “on”, while several planned hydro dams are now “off”.
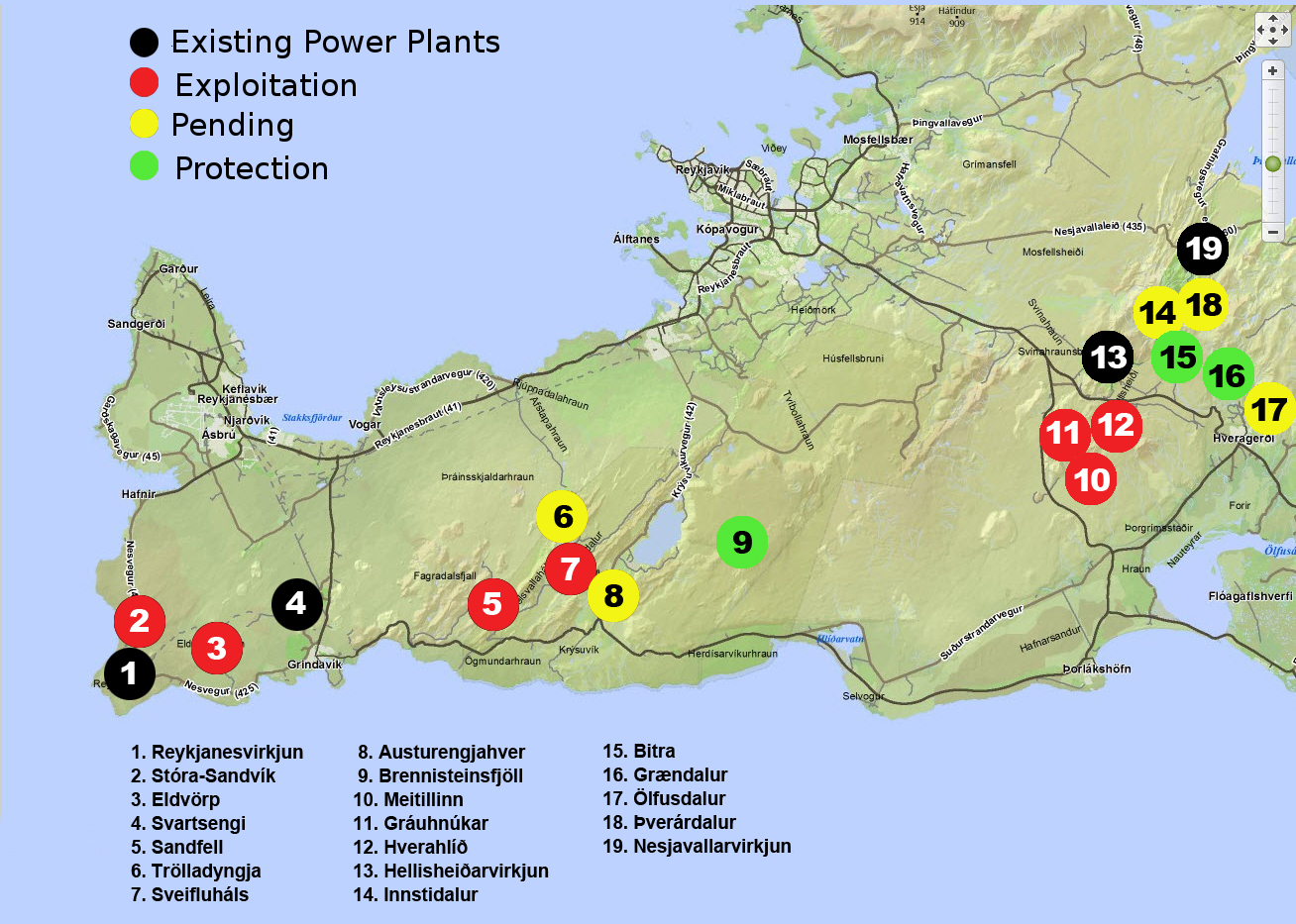
Effluent lagoons have already been discovered at test drilling sites at Þeistareykir and Bjarnarflag in the North9. If all of the planned geothermal power plants are built around Mývatn, the town of Reykahlíð will become exposed to 32,000 tons of hydrogen sulphide per year potentially raising serious health issues for residents10. In Reykjanes the two existing geothermal power plants at Svartsengi and Rekjanesvirkjun already produce huge amounts of hydrogen sulphide, and the proposed expansions and new projects would radically increase this figure. Scientists have warned that geothermal fields at Svartsengi are already overexploited and may not be able to produce power much longer11. In addition many of the new proposed drilling sites are connected to the same geothermal aquifer and could very quickly become dried or cooled by excessive exploitation for large scale energy. For further information read Saving Iceland’s detailed account of the planned geothermal power projects on Reykjanes peninsula.)
The fact is that geothermal energy technology is still very new and little is known about the long term, or even short term effects of exploiting the heat of volcanic aquifers on such a large scale. In addition, geothermal areas are globally incredibly rare and each one is different, making the impacts of drilling and power generation hard to predict. Cambridge University professor David McKay’s comprehensive 2009 book on sustainable energy points out that geothermal power is neither sustainable nor renewable when used on a commercial scale as the wells can quickly dry up or cool down, taking more than a hundred years to recover afterwards12, yet drastically altering the local environment. Experimenting with such an undeveloped technology in Iceland’s endemic geothermal hot spring areas, which the country is so famous for, could result in total destruction of these beautiful and unique places. All that for only a few years of energy production, which in turn would be sold at a cut rate price to heavy industry, reaping little reward for Icelandic people.
See Saving Iceland’s photos of the effects of drilling at Hellisheiði here. The photos are from 2008 when Saving Iceland’s then annual action camp against heavy industry was located at Hellisheiði. Read More